PLUS ONE COMPUTER SCIENCE
First Year Computer Science Previous Questions Chapter wise ..
Chapter 8. Arrays
1. An array is declared as follows:
int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
What will be the value of a[2] + a[3]?
a) 7
b) 5
c) 6
d) 4
Ans. a
2. Write C++ statements to double each element of the array int A[100].
3. Consider an array A with the following elements sorted in ascending order.
5, 9, 10, 13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 25, 37
Explain the working of binary search algorithm to search 25. How many comparisons
are required for this searching?
4. Find the value of score[4] based on the following declaration statement:
int score[5] = {98, 87, 92, 79, 85};
Ans. 85
5. Suppose M[5][5] is a 2D array that contains the elements of a square matrix. Write C++
statements to find the sum of the diagonal elements.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ int mat[5][5], n, i, j, s=0;
cout<<"Enter the rows/columns of square matrix: ";
cin>>n;
cout<<"Enter the elements\n";
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
for(j=0; j<n; j++)
cin>>mat[i][j];
cout<<"Major diagonal elements are\n";
for(i=0; i<n; i++)
{
cout<<mat[i][i]<<"\t";
s = s + mat[i][i];
}
cout<<"\nSum of major diagonal elements is: ";
cout<<s;
return 0;
}
6. Write an algorithm for arranging elements of an array in ascending order using bubble
sort.
Step 1. Start
Step 2. Accept a value in N as the number of elements of the array
Step 3. Accept N elements into the array AR
Step 4. Repeat Steps 5 to 7, (N - 1) times
Step 5. Repeat Step 6 until the second last element of the list
Step 6. Starting from the first position, compare two adjacent elements in the
list. If they are not in proper order, swap the elements.
Step 7. Revise the list by excluding the last element in the current list.
Step 8. Print the sorted array AR
Step 9. Stop
7. ………………. search method is an example for ‘divide and conquer method’.
Ans. Binary search
8. What is an array? Write C++ program to declare and use a single dimensional array for
storing the computer science marks of all students in your class.
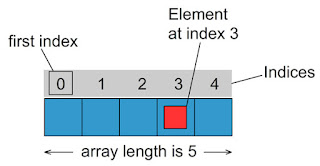
An array is a collection of elements of the same type placed in contiguous memory locations. Arrays are used to store a set of values of the same type under a single variable name. Each element in an array can be accessed using its position in the list called index number or subscript.
9. a) Write C++ program for sorting a list of numbers using Bubble sort method.
b) Write different passes of sorting the following numbers using Bubble sort:
32, 21, 9, 17, 5
Ans. a.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int AR[25],N;
int I, J, TEMP;
cout<<"How many elements? ";
cin>>N;
cout<<"Enter the array elements: ";
for(I=0; I<N; I++)
cin>>AR[I];
for(I=1; I<N; I++)
for(J=0; J<N–I; J++)
if(AR[J] > AR[J+1])
{
TEMP = AR[J];
AR[J] = AR[J+1];
AR[J+1] = TEMP;
}
cout<<"Sorted array is: ";
for(I=0; I<N; I++)
cout<<AR[I]<<"\t";
}
10. Declare a two dimensional array to store the elements of a matrix with order 3 x 5.
Ans. int M[3][5];
11. Define an array. Also write an algorithm for searching an element in the array using any
one method that you are familiar with.
An array is a collection of elements of the same type placed in contiguous memory
locations. Arrays are used to store a set of values of the same type under a single variable
name. Each element in an array can be accessed using its position in the list called index
number or subscript.
Algorithm for Linear Search
Step 1. Start
Step 2. Accept a value in N as the number of elements of the array
Step 3. Accept N elements into the array AR
Step 4. Accept the value to be searched in the variable ITEM
Step 5. Set LOC = -1
Step 6. Starting from the first position, repeat Step 7 until the last element
Step 7. Check whether the value in ITEM is found in the current position. If found then
store the position in LOC and Go to Step 8, else move to the next position.
Step 8. If the value of LOC is less than 0 then display "Not Found", else display the
value of LOC + 1 as the position of the search value.
Step 9. Stop
12. int num[10];
The above C++ statement declares an array named num that can store maximum ….
integer location.
a) 9
b) 10
c) N
d) none of these
Ans. b
13. Explain the memory allocation for the following declaration statement.
int A[10][10];
14. Write a C++ program to illustrate array traversal.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[10], i;
cout<<"Enter the elements of the array :";
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
a[i] = a[i] + 1;
cout<<"\nEntered elements of the array are...\n";
for(i=0; i<10; i++)
cout<< a[i]<< "\t";
return 0;
}
15. Read the following C++ statement:
int MAT[5][4];
(a) How many bytes will be allocated for this array?
(b) Suppose MAT[4][4] is a 2D array that contains the elements of a square matrix.
Write C++ statements to find the sum of all the elements in the array.
Ans.
a. 4*5*4=80 bytes
16. Write the names of two searching methods in arrays. Prepare a chart that shows the
comparison of two searching methods.
Linear search and Binary search.
Linear search method Binary search method
• The elements need not be in any order • The elements should be in sorted order
• Takes more time for the process • Takes very less time for the process
• May need to visit all the elements • All the elements are never visited
• Suitable when the array is small • Suitable when the array is large