PLUS TWO COMPUTER SCIENCE
Chapter 3. Data Structures and Operations
(+2. Computer Science Questions and answers from text book)
1. Define data structure?
Data structure is a particular way of organising logically related data items which can be
processed as a single unit.Depending upon memory allocation, data structures may be classified as static data
structures and dynamic data structures. Memory allocation is fixed for static data
structures (eg: arrays) and the size cannot be changed during execution. Memory is
allocated during execution for dynamic data structures (eg: linked list) and the size changes
according to the addition or deletion of data items.
2. Stack follows ------------- principal for organising data.
Ans. LIFO
3. Name the data structure that follows FIFO principal.
Ans. Queue.
4. What is meant by underflow?
If we try to
delete an item from an empty stack, an unfavourable situation arises, known as stack underflow. If we attempt a
deletion from an empty queue, underflow occurs.
5. Which element of stack can be deleted first or last.
Ans. First
6. Name an example for dynamic data structure.
Ans. Linked list
7. What is linked list?
Linked list is a collection of nodes, where each node consists of two parts – a data and a
link. Link is a pointer to the next node in the list. The address of the first node is stored in a
special pointer called START. Linked list is a dynamic data structure. Memory is allocated
during run time. So there is no problem of overflow. It grows as and when new data items
are added, and shrinks whenever any data is removed. Linked list is created with the help of
self referential structures.
8. A node of linked list consists of ------------- and -------------.
Ans. Data and Link
9. Which is the facility of programming language used to define the node of a linked list?
Ans. Pointer
10. What is the content of Start and Header of a linked list.
Ans. Start or Header is the address of the content of the first node.
11. What are the application of queue?
Serving requests on a single shared resource, like a printer, CPU task scheduling etc. In real life scenario, Call Center phone systems uses Queues to hold people calling them in an order, until a service representative is free. Handling of interrupts in real-time systems.
12. What is traversing?
12. What is traversing?
Traversing is an operation in which each element of a data structure is visited.
13. What is merging?
Merging is the process of combining elements of two sorted data structures to form a new one.
14. What is meant by Stack overflow?
It is the process of inserting a new data item into the stack at Top position.
Once the stack is full and if we attempt to insert an item, an impossible situation arises,
known as stack overflow.
15. Explain the classification of compound data structures?
compound data structure divided into two types
a) Linear Data Structure and b) Non Linear Data Structure.
A Linear data structure have data elements arranged in sequential manner and each member element is connected to its previous and next element. ... Such data structures are easy to implement as computer memory is also sequential. Examples of linear data structures are List, Queue, Stack, Array etc.
16. Different type of linked list?
Singly Linked List
It is the most common. Each node has data and a pointer to the next node. 
Circular Linked List
A circular linked list is a variation of a linked list in which the last element is linked to the first element. This forms a circular loop.
It is the most common. Each node has data and a pointer to the next node.

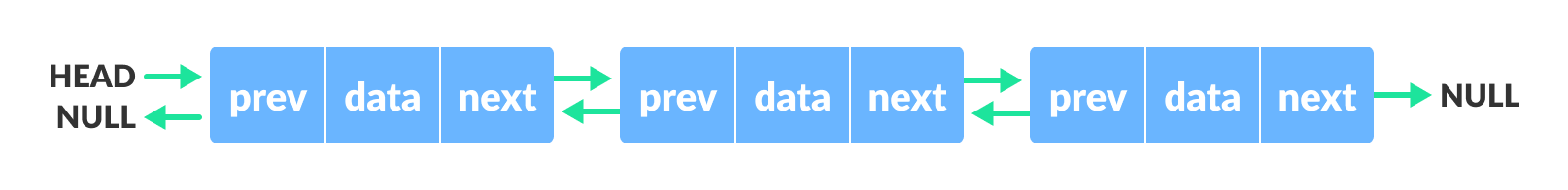
Doubly Linked List
We add a pointer to the previous node in a doubly-linked list. Thus, we can go in either direction: forward or backward.
We add a pointer to the previous node in a doubly-linked list. Thus, we can go in either direction: forward or backward.
Circular Linked List
A circular linked list is a variation of a linked list in which the last element is linked to the first element. This forms a circular loop.